Vascular Dementia: Neglected Killer
Preface
When it comes to dementia, we tend to think of Alzheimer’s disease, a widely known dementia that steals the thunder of the whole dementia family. Today, however, we are going to introduce a lesser known but equally intractable dementia, the vascular dementia. Its onset ages are earlier than Alzheimer’s, sometimes even at 20; therefore, the disease is easily neglected, but no less fatal than its counterpart.
Symptoms and Subtypes
Subtypes of dementia include the Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies, frontotemporal dementia, and diabetes-induced cognitivedysfunction—diabetic dementia; the Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia account for more than 80% of the existing dementia cases.
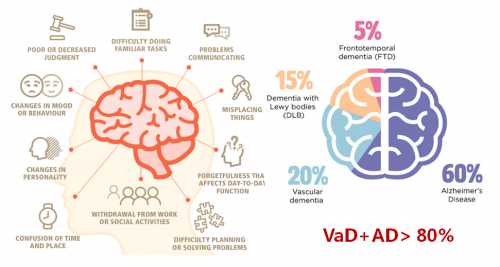
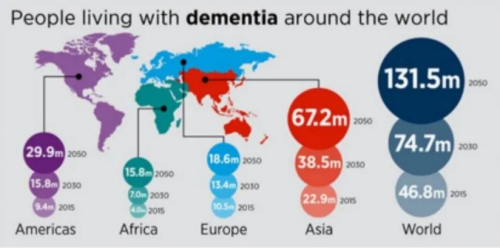
The Reality Worldwide
It’s estimated that the year 2050 will witness 135 million dementia sufferers worldwide and 30 million of them will be affected by vascular dementia.
In December 2020, the largest existing study on dementia prevalence was published by a research team led by Prof. Jianping Jia, a neurological expert from Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University, on the Lancet Public Health(a specialty journal under The Lancet). With a thorough research on the prevalence, risk factors and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 or above in China, the article estimates that, with approximately 15.07 million patients, the prevalence rate stands at 6.0% for dementia, 3.9% for Alzheimer’s disease, 1.6% for vascular dementia, and 0.5% for other dementias. That said, there are about 4 million patients with vascular dementia in the country, and the prevalence rate of vascular dementia will surge in the consequently with the aging of population and increasing incidence of cerebrovascular cases.
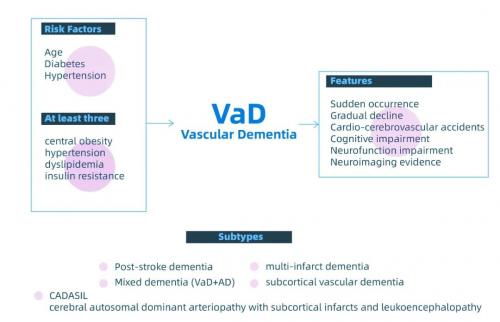
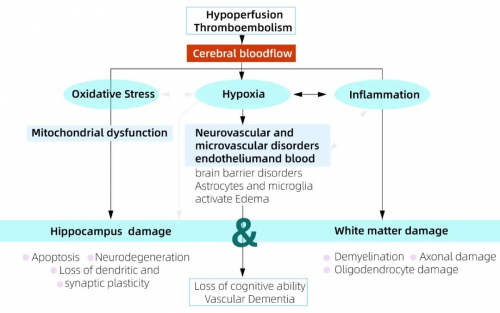
Vascular Dementia (VaD), also known as Vascular Cognitive Impairment (VCI), is a dementia caused by impaired cerebral blood flow, leading to memory and cognitive dysfunctions.
Main causes of vascular dementia include cerebral hemorrhage and cerebral infraction. Since the incidence of these two diseases is increasing among young people, age range of vascular dementia is consequently shifting towards younger trend.
Though 20-year-old patients with vascular dementia are extreme cases, patients aged between 30 and 40 are not uncommon, and quite often, clinics receive patients whose dementia worsens for lack of timely intervention on their hypertension. Young patients with hypertension and hyperglycemia often fail to achieve timely intervention and medication.
What’s worse, they have to suffer the diseases much longer than the elderly, which increases the incidence and severity of other complications, along with heavier disease burdens. In this sense, vascular dementia can be more dangerous than the Alzheimer’s.
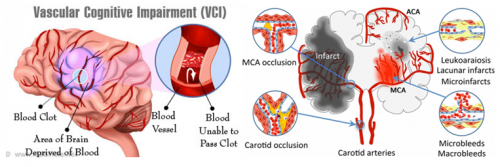
Symptoms
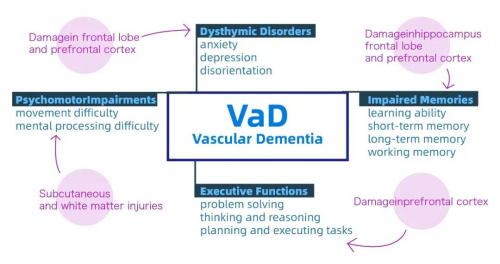
Risk Factors, Features and Subtypes
Pathogenesis
Four numbers to be alerted within the medical examination report
A: Blood pressure 130
"130" refers to people with systolic blood pressure ≥ 130 mmHg, in other words, people with high blood pressure levels, which may result in cerebrovascular diseases. The diagnostic standard for hypertension is 140/90 mmHg; however, people with blood pressures lower than 140/90 mmHg may stil l be highly subject to cerebrovascular disease.
B: Homocysteine 15
The "15" refers to a blood level of homocysteine (Hcy) of 15 μmol/L. Elevated homocysteine (Hcy) may also trigger cerebrovascular disease. High homocysteine can cause damage in endothelial cells, stimulate blood vessels, increase cardiac smooth muscle cells, and lead to thickening of blood vessel walls; it may also promote the expression of thrombomodulin, making the blood get coagulated easily. Hcy not only causes various damage to blood vessels, but also amplifies the damage to blood vessels and body caused by hypertension, dyslipidemia, obesity, and abnormal blood sugar.
C: Body mass index 28
One with a BMI (Body Mass Index) at 28 or above is reckoned obese. Obesity leads to high blood lipids in blood vessels, which may cause atherosclerosis! This will increase the risks of cerebral thrombosis, cerebral hemorrhage, stroke and other causative factors for vascular dementia.
D: Fasting blood glucose 5.9
“5.9”refers to a fasting blood glucose value of 5.9 mmol/L. High blood glucose also affects cerebrovascular health. People with pre-diabetes need to control their blood glucose to prevent diabetes and cerebrovascular damage, thus staying safe from vascular dementia.
Treatment of vascular dementia
There is no specific treatment for vascular dementia, and the FDA hasn't approved any vascular dementia drugs yet. The main treatment measures include early diagnosis, control of risk factors, cognitive improvement therapy and symptomatic treatment. Prevention is the fundamental approach to the prevention and treatment of vascular dementia. Cholinesterase inhibitors such as donepezil, carboplatin, and stigmasterol have been proved effective by many clinical studies in improving cognitive function and basic living abilities in patients with mild to moderate vascular dementia. Memantine has been approved for the treatment of moderate and severe AD in the United States and Europe and can also be used for vascular dementia. However, drugs for AD have limited effect on vascular dementia. Other drugs such as butalbital (phase II/III clinical), cerebrolysin (phase II clinical), TMBCZG (phase II clinical), nicergoline, ginkgo biloba extract, piracetam and some proprietary Chinese medicines and herbal tonics may have adjuvant therapeutic effects on improving patients' cognitive functions, but this remain to be proved by further clinical trials.
Afterword
Chinese guideline for diagnosis and treatment of dementia and cognitive disorders (2019)points out that there are seven risk factors, based on big data and computer modeling analysis, most significant in preventing dementia. Proper control of the seven factors may help reduce occurrence of dementia, in particular vascular dementia, by one third globally. The seven factors are obesity, hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, smoking, low education level and cardiovascular disease.
To prevent the risks, a healthy lifestyle is also necessary besides promoted education levels. This includes:
A moderate amount of exercises. 3 to 5 times of moderate-intensity activities per week, 30 to 60 minute each time.
A healthy diet. Keeping a low-carbon diet and maintain a reasonable dietary structure (reference to the Mediterranean Diet, DASH Diet or other recognized healthy eating patterns).
Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Enough sleep, at least 7-8 hours a day (adults).
References
1.Jia L, et al. COAST Group. Prevalence, risk factors, and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Public Health. 2020 Dec;5(12): e661-e671.
2.Venkat P, Chopp M, Chen J. Models and mechanisms of vascular dementia. Exp Neurol. 2015 Oct; 272:97-108.
Editor:Alan Wang
Translator:April
Auditor:Jane Lee




本文网址:http://ttkbao.com/news/26249.html
声明:本站原创/投稿文章所有权归天天快报所有,转载务必注明来源;文章仅代表原作者观点,不代表天天快报立场;如有侵权、违规,可直接反馈本站,我们将会作删除处理。
网友评价

来自广西壮族自治区梧州市的热心网友评价:
有用
 347
347

来自广东省梅州市的热心网友评价:
内容正在审核中……
 347
347

来自河北省沙河市的热心网友评价:
啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊啊vlog!!!
 347
347

来自黑龙江省北安市的热心网友评价:
哈哈哈哈 开心就好
 347
347

来自辽宁省沈阳市的热心网友评价:
来啦!!
 347
347
新闻
更多>>
国际知名口腔博士穆巴拉克与格伦菲尔顺利签约,共促口腔医疗新发展
-
[今日头条]
柯岩新胜幼儿园开展了民间游戏活动...
-
[今日头条]
俏生元呵护冬日肌肤健康,满足女性多场景护肤需求...
汽车
更多>>-

新车保养注意事项需了解,让车主养成良好驾驶习惯
2023-05-15
-

全球快讯:Stellantis任命新CFO 将于7月10日到任
2023-05-04
-

奇瑞首个新能源电动品牌iCAR携“双车”亮相
2023-04-19
-

加速能源和产业生态布局,广汽集团将发布e-TIME行动
2023-04-18
-

奥特能平台车型,大五座SUV别克ELECTRA E5向智电而生
2023-04-17








